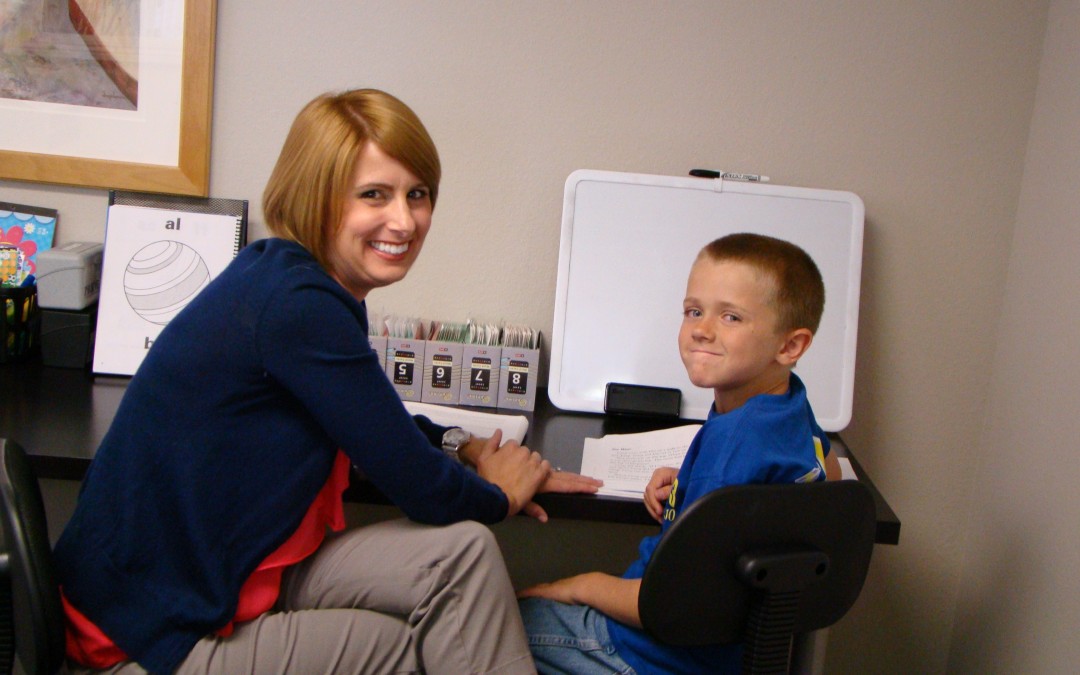
by PRIDE Reading Program Admin | Feb 19, 2016 | Pride Yorba Linda, Summer Programs
PRIDE Learning Center, a dyslexia tutoring company, will be expanding its services to the Yorba Linda community this summer for the second year. This reading camp is aimed at students from 4-18 years old who have specific learning disabilities with reading, writing and comprehension. Students will attend sessions from 9:00am – 12:00pm Monday through Friday or from 12:30 – 3:30 Monday – Friday.
The dyslexia summer camp at PRIDE Learning Center includes one-on-one tutoring using the Orton-Gillingham approach with reading, writing and comprehension lessons. One of the most highly effective methods for teaching students with Dyslexia is the Orton-Gillingham approach. It teaches the structure of the language using various multisensory techniques that encourage students to see, hear and write a concept at the same time.
“We often see our campers making one to two years worth of progress during our 4-6 week summer camps,” says PRIDE Learning Center’s Director Karina Richland. “The Orton-Gillingham program is like a life-saver for dyslexic kids. Many of them have tried so many different programs and this is finally the one that works for them,” says Richland.
PRIDE Learning Center’s summer dyslexia camp will be held at 19045 Yorba Linda Blvd in Yorba Linda. There is limited space available and early registration is recommended. For more information visit the PRIDE Learning Center website at www.pridelearningcenter.com or call 866-774-3342.

by PRIDE Reading Program Admin | Feb 17, 2016 | Articles & Resources
A summer camp for students with dyslexia or dyspraxia will be offered this summer in Sherman Oaks, California.
PRIDE Learning Center, a dyslexia tutoring company, will be expanding its services to the Sherman Oaks community this summer. This summer reading camp is aimed at young people from 4-18 years old who have specific learning disabilities with reading, writing and comprehension. Students will attend sessions from 9:00am – 12:00pm Monday through Friday or from 12:30 – 3:30 Monday – Friday.
The summer reading camp at PRIDE Learning Center includes one-on-one tutoring using the Orton-Gillingham approach with reading, writing and comprehension lessons. One of the most highly effective methods for teaching students with Dyslexia is the Orton-Gillingham approach. It teaches the structure of the language using various multisensory techniques that encourage students to see, hear and write a concept at the same time.
“We often see students making one to two years worth of progress during our 4-6 week summer camps,” says PRIDE Learning Center’s Director Karina Richland. “The Orton-Gillingham program is like a life-saver for dyslexic kids. Many of them have tried so many different programs and this is finally the one that works for them,” says Richland.
PRIDE Learning Center summer camp will be held at 14960 Ventura Blvd in Sherman Oaks, Ca. There is limited space available and early registration is recommended. For more information visit the PRIDE Learning Center website at www.pridelearningcenter.com or call 866-774-3342.

by PRIDE Reading Program Admin | Feb 15, 2016 | A PRIDE Post, Learning Disabilities, Reading Comprehension, Reading Skills
Reading is a highly complex, integrated activity that daunts as many as 33 percent of the population. Many children become proficient readers regardless of how they are taught. However, for children who experience difficulty learning to gain meaning from print, reading must be systematically and carefully taught. Mastering the following components of the reading process is essential if students are to become proficient readers.
Appreciation and enthusiasm for reading
It comes as no surprise that children who are passionate about reading are more skillful readers. Reading is more exciting to students when they are:
Read to frequently
Allowed to choose their reading material
Exposed to a wide variety of interesting reading materials
Phonemic awareness
Successful reading depends upon understanding that words are composed of individual sounds. Children need direct teaching in the skills of breaking words into their component sounds and in blending individual sounds together into words. Phonemic awareness is one of the most important skills upon which early reading depends. Children who have poorly developed phonemic awareness skills are at great risk for becoming poor readers.
Phonics and Decoding
Letters of the alphabet are a code representing the sounds in words. Reading involves “decoding” or translating written words into their spoken equivalents. The early stage of decoding instruction emphasizes the correspondence between individual letters or pairs of letters (such as “oa”) and the sounds they represent. Later reading instruction stresses rapid identification of larger units such as syllables. Identifying larger phonetic elements is termed structural analysis. Once a student learns the correspondence between sounds and print, he or she has become a proficient decoder.
Fluent, Automatic Reading of Text
However, in order to become an efficient reader, the decoding process must become fast and accurate. When decoding is efficient, attention and memory processes are available for comprehending what is being read. Reading fluency training is vital for strengthening a student’s comprehension skills. Children should have ample practice reading material that is not difficult for them to decode. This level is referred to as the “independent reading level.” Frequent reading of material at a child’s independent reading level builds automatic word recognition and frees up a child’s mental abilities for comprehension.
Background Knowledge
Comprehension depends heavily on a student’s knowledge of the world. Therefore, the skill of reading comprehension begins to develop long before children enter school. Children who have more experiences of all types, have more background knowledge upon which to base their understanding of written material. Parents help their child develop reading skills when they visit the museum, the park and even the store. Parents and teachers should also read to students in order to help them create a stockpile of information that will facilitate reading comprehension. The best reading instruction teaches a student to access background knowledge while reading.
Vocabulary
Comprehension depends on having a large vocabulary. Children who read widely learn word meanings at a faster rate than children whose reading is more limited either in scope or quantity. During their school years, children should be learning several thousand new words per year. Most of these words are learned by reading.
Written Expression
Reading and writing are two sides of the same coin. Effective reading instruction must include training in expressing one’s thoughts in writing. Children should be given daily practice in organizing and expressing their knowledge through writing. This builds their ability to decode and comprehend the thoughts of other writers.
The key to helping students who experience difficulty in learning to read is to identify a student’s specific reading problems and devise programs which capitalize upon a student’s unique learning strengths. A curriculum that focuses on specific, appropriate, and practical learning strategies will best help students become proficient, efficient and independent readers.
An appropriate literacy goal for all students should be that each is fully able to use reading as a springboard for independent, critical thought and expression. Reading fuels the highest levels of the thinking process. Good readers are armed with tools to become strong thinkers.
Learn more about the New PRIDE Reading Program
________________________________________________________________
Dr. Kari Miller is a board certified educational therapist and director of Miller Educational Excellence, a full-service educational therapy facility in west Los Angeles.
You can visit her website at www.MillerEducationalExcellence.com or email her at klmiller555sbcglobal.net

by PRIDE Reading Program Admin | Feb 8, 2016 | A PRIDE Post, Reading Fluency, Reading Skills
Reading is a skill that needs to be practiced regularly. Without practice, young readers will not develop the vocabulary, the skills, and the fluency necessary to become strong readers. But many children, even those with strong reading skills, do not get enough practice and as a result become disinterested in reading, and can quickly become discouraged. Here are some practical tips for when your chid doesn’t want to read:
- Find books with cartoons or humor — which only a child would find amusing.
When your child doesn’t want to read… don’t make everything a learning lesson. Letting children read books such as Captain Underpants or Diary of a Wimpy Kid will keep them engaged and entertained. Although adults might find the language and humor distasteful, children find it very funny and are therefore more motivated to read.
- Zero in on your child’s passions and choose books and magazines focused on areas of interest.
If your child doesn’t want to read try finding books on specific topics to keep your child’s interest, such as science, baseball, American Girl dolls, etc. Children who already have the background knowledge, language and vocabulary before beginning a book will have an easier time getting through the reading. Order a magazine subscription to Sports Illustrated for Kids or Nickelodeon. Children love receiving mail and reading ‘their’ magazines.
- Get your child an email account and, together, check it regularly.
Using the computer to read and write is a huge advantage for most students. By letting young children write and send email, they practice reading, writing and spelling. Teach your child how to use spell check before sending off messages. Be sure to monitor your child’s ‘pen pals’ – who is your child writing to and receiving mail from? Let your child pick out a few family members, including grandparents and maybe two or three friends. You will find that by using email regularly, your child becomes very strong in typing (keyboarding) and using the computer.
- Find an author that your child likes and stick with it.
If your child loves reading Hank Zipzer by Henry Winkler or Tales of a Fourth Grade Nothing by Judy Blume, then you have found a writing style which stimulates your child’s interest. Go through the entire series. Don’t worry if the reading is below grade level: your child is reading for pleasure and for practice. Also remember, just because you loved a certain author or series when you were a kid, this doesn’t mean your child will love the same books you did. Browse the bookstore or library and find the newest, most modern series. Usually these books contain language and themes to motivate the most reluctant reader. Kids need to relate to what they are reading, and modern language usage helps.
- Let your child talk to you about the book they are reading.
When we adults read books we enjoy, we like to talk about them. After reading a book, we don’t necessarily want to write a summary, book report or make a project of it. We just want to discuss it with someone else. Look interested in what your child is reading (yes, even if it is Captain Underpants) and ask questions and have your child tell you about it. Laugh with your child about the funny parts (even at the bathroom jokes) and help your child feel good about reading.
Learn more about the New PRIDE Reading Program
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Karina Richland, M.A., E.T. is the Managing Director of Pride Learning Centers, located in Los Angeles and Orange County. Ms. Richland is a reading and learning disability specialist. Ms. Richland speaks frequently to parents, teachers, and professionals on learning differences, and writes for several journals and publications. You can visit the Pride Learning Center website at: www.pridelearningcenter.com

by PRIDE Reading Program Admin | Jan 31, 2016 | A PRIDE Post, Orton-Gillingham
Learning to read in English would be such a simple task if all similar-sounding phonemes were spelled the same. They aren’t. English is such an unfair language with so many iniquitous rules! For most of us, learning to read means memorizing the symbolic code of letter combinations and then using them in new contexts. Many of us just read naturally, understanding that these letter combinations create words and sounds. Linguists call these sounds ‘phonemes.’ Our brains just register the words and are equipped to read three or four words ahead of time. We are also mentally able to pull words apart, separate them into syllables and apply all of those unfair spelling rules easily and logically.
For a student with a reading disability, this process of reading does NOT come naturally. Students with dyslexia, for example, do not use the process of sounding out phonemes (decoding) while reading and applying spelling rules while writing (encoding). Dyslexics, in general, memorize words in entirety and make mental pictures of each word they learn. The predicament with this strategy is that when they get to a word that they are unfamiliar with, they have no coping mechanisms to attack that particular word.
An example of the difficulty for some of us to learn which combination of letters creates which phoneme is the sound of the letter ‘a’ as in the word ‘cake.’ The long ‘a’ sound is written differently in different words, as in baby, ape, sail, play, steak, vein, eight and they. For students with reading disabilities, something interferes with the acquisition of these written phonemes, and in order to learn, these students must be taught how to read in a different way. One such way is using a multi-sensory method.
Students with a reading disability often struggle with auditory and/or visual processing. They have troubles recalling words and how they are pronounced. This means that they do not comprehend the roles that sounds play in words. These students have difficulties rhyming words as well as blending sounds together to form words. These students do not understand or acquire the alphabetic system expected of them in the early years. If a student with a learning difference is given a task that uses just hearing and vision, without drawing upon other senses, this student will be at a disadvantage. When taught with a multi-sensory approach, students will learn alphabetic patterns, phonemes and words by utilizing all pathways – hearing (auditory), seeing (visual), touching (tactile) and moving (kinesthetic).
When learning the vowel combination ‘oa,’ for example, the student might first look at the letter combination on a picture of a GOAT, then close his/her eyes and listen to the sound, then trace the letters in the air while speaking out loud. This combination of listening, looking, and moving around creates a lasting impression for the student as things will connect to each other and become memorable. Using a multi-sensory approach to reading will benefit ALL learners, not just those with reading disabilities.
The other significant component in helping a struggling reader learn to read and write is utilizing an Orton-Gillingham approach. In Orton-Gillingham, the phonemes are introduced in a systematic, sequential and cumulative process. The Orton-Gillingham teacher begins with the most basic elements of the English language. Using repetition and the sequential building blocks of our language, phonemes are taught one at a time. This includes the consonants and sounds of the consonants. By presenting one rule at a time and practicing it until the student can apply it with automaticity and fluency, students have no reading gaps in their word-decoding skills. As the students progress to short vowels, they begin reading and writing sounds in isolation. From there they progress to digraphs, blends and diphthongs.
Students are taught how to listen to words or syllables and break them into individual phonemes. They also take individual sounds and blend them into a word, change the sounds in the words, delete sounds, and compare sounds. For example, “…in the word steak, what is the first sound you hear? What is the vowel combination you hear? What is the last sound you hear? Students are also taught to recognize and manipulate these sounds. “…what sound does the ‘ea’ make in the word steak? Say steak. Say steak again but instead of the ‘st’ say ‘br.’- BREAK!
Every lesson the student learns is in a structured and orderly fashion. The student is taught a skill and doesn’t progress to the next skill until the current lesson is mastered. As students learn new material, they continue to review old material until it is stored into the student’s long-term memory. While learning these skills, students focus on phonemic awareness. There are 181 phonemes or rules in Orton-Gillingham for students to learn. Advanced students will study the rules of English language, syllable patterns, and how to use roots, prefixes, and suffixes to study words. By teaching how to combine the individual letters or sounds and put them together to form words and how to break longer words into smaller pieces, both synthetic and analytic phonics are taught throughout the entire Orton-Gillingham program.
Students with reading disabilities need more structure, repetition and differentiation in their reading instruction. They need to learn basic language sounds and the letters that make them, starting from the very beginning and moving forward in a gradual step by step process. This needs to be delivered in a systematic, sequential and cumulative approach. For all of this to “stick” the students will need to do this by using their eyes, ears, voices, and hands.
Learn more about the New PRIDE Reading Program
__________________________________________________________________________________
Karina Richland, M.A. is the Managing Director of Pride Learning Centers, located in Southern California. Ms. Richland is a reading and learning disability specialist. She speaks frequently to parents, teachers, and professionals on learning differences, and writes for several journals and publications. You can visit the website www.pridelearningcenter.com





